Maggie/Mechanics
De Wikidroids
Sommaire |
Mechanical concept
The chassis of Maggie is made only of aluminium and PCB parts. This makes a very lightweight and robust construction.
Fichier:Maggie motor dimension.pdf
These are the parts of Maggie :
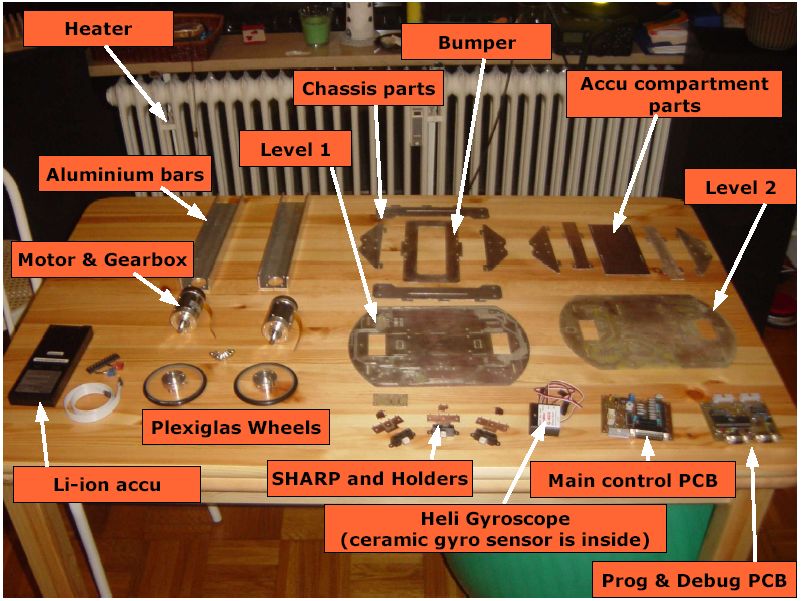
Aluminium part of the chassis and propulsion
The aluminium part of the chassis is the main skeleton. it is composed of 4 'L' bars put vertically
The motorisation is composed of brushless motors (Maxon EC45 30W with sensors) adapted to gearboxes (Dunkermotoren PLG42S 1:16)

The gears are oversized, this is done for robustness. In theory we can put 30 kg of weight onto Maggie. The wheels are made of a plexiglas plate turned on a lathe, and fixed to an aluminium part. The contact to the floor is made with a toroidal joint.
PCB part of the chassis
The PCB parts (including tracks) are milled with an LPKF PCB milling machine. This allows to make really complicated 2D parts.
The PCB chassis has two levels. Each is a horizontal PCB, with some traces and components.
Under each level, clipsed PCBs make the link to the aluminium chassis, and avoid bending f the level.
The level 1 contains the LED belt, the sharp sensors, the Prog and control PCBs, and the link to the gyro.
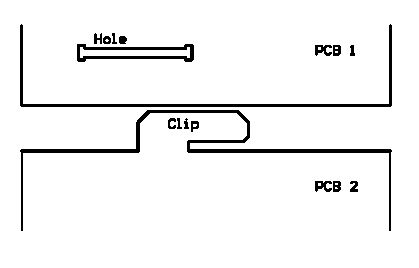
PCB clips
The PCBs are hooked together with hooks (clips) and holes that are milled into the PCBs.
Principle of these clips :
The PCB 2 is simply inserted in the hole, and then shifted.
Example of clip on Maggie :
This makes a robust assembly of the two PCBs. There must be another element which locks the shifting of the clips. This is sometimes made with the aluminium bars passing through(for the levels) or simply with a solder point between the two PCBs (for accu housing).